Voltage at the v cc pin at the inverter no decoupling caps notice the peak to peak voltage fluctuations of 158 v. Figure 14 shows the voltage measurement at the v cc pin of the inverter with the decoupling capacitors.

Bypass Caps Decouple Your Way To Cleaner Power

Need Of Decoupling Capacitor

Map Of Voltage Drops Within The Sample Circuit For Two
A decoupling capacitor acts as a local electrical energy reservoir.
Decoupling capacitor voltage drop. The capacitor is meant to cancel out any current fluctuations on your power rail so that they do not affect the voltage seen by an ic. Adding the bypass capacitor supplies the 74hc04 with instantaneous power for the duration. We have seen decoupling capacitors are used to block voltage fluctuations or in other words it helps to block ac signals since fluctuation or voltage drop is a form of ac signal since the voltage of the signal varies over time.
Once completely charged the decoupling capacitor opposes any change in the voltage across it by providing discharging if the voltage drops or vice versa. Figure 13 shows the voltage measurement at the v cc pin of the inverter with no decoupling capacitors. The capacitor stores a small amount of energy that can compensate for the voltage drop in the power supply conductors to the capacitor.
Decoupling capacitors act as local energy reservoirs to prevent the ic from experiencing a voltage drop. Decoupling capacitors alone may not suffice in such cases as a high power amplifier stage with a low level pre amplifer coupled to it. This is useful when multiple parts of the circuit are pulling from the same power supply at the same time and they cannot all be supported.
In digital circuits decoupling capacitors also help prevent radiation of electromagnetic interference from relatively long circuit traces due to rapidly changing power supply currents. Coupling capacitor on the other hand blocks the dc signal while allowing ac signal to pass through. Measuring the probability of generating a functional failure depends on the value of the decoupling capacitor 50 nf or 68 nf on the frequency of the d flip flop 25 and 10 mhz and on the magnitude of the tlp pulse from 10 v to 200 v.
Capacitors like batteries need time to charge and discharge. If the input voltage suddenly drops the capacitor provides the energy to keep the voltage stable. This prevents rc delays that could be caused from the voltage drooping.
The bypass capacitor is about 4000 times as large as the load capacitance which means that the expected voltage drop will be some 4000 times lower in the order of 12mv to support the transition. In digital circuits decoupling capacitors also help prevent radiation of electromagnetic interference from relatively long circuit traces due to rapidly changing power supply currents. The capacitor stores a small amount of energy that can compensate for the voltage drop in the power supply conductors to the capacitor.
When used as decoupling capacitors they oppose quick changes of voltage. Similarly if there is a voltage spike the capacitor absorbs the excess energy.

Bypass Caps Decouple Your Way To Cleaner Power

Impact Of A Decoupling Capacitor In A Cmos Inverter Circuit

Ppp Based Rbb Decoupling Capacitor Voltage And Voltage

Decoupling Capacitor Wikipedia

Pdf Time And Frequency Domain Analysis Of Integral

What Happens If A Coupling Capacitor Is Not Used For

Impact Of A Decoupling Capacitor In A Cmos Inverter Circuit

Ferrite Beads For Filtering Power Intentional Logic

Decoupling Capacitor An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The Decoupling Capacitor Is It Really Necessary Precision
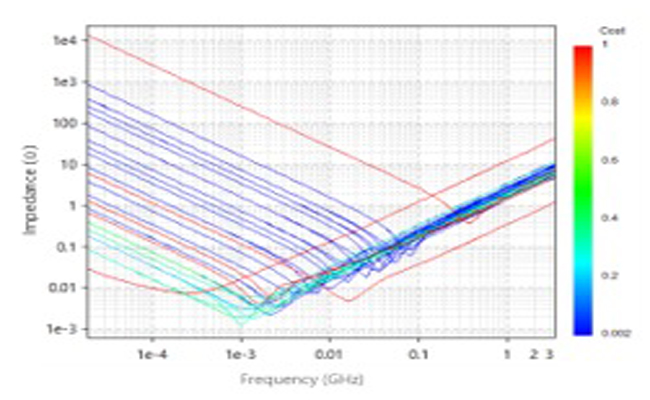
Power Integrity
Power Integrity Is More Than Decoupling Capacitors The
Comments
Post a Comment